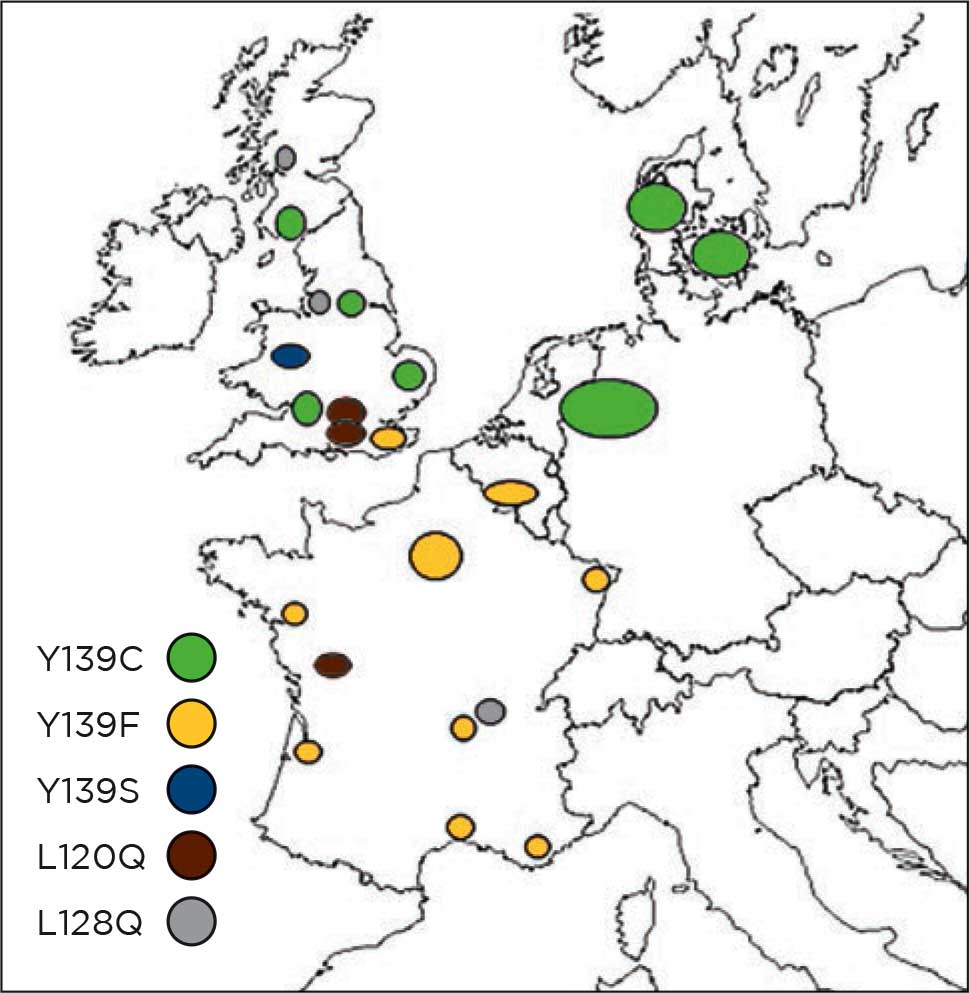
The different resistance SNPs confer on the animals that carry them different degrees of resistance to anticoagulants. Generally, possession of a resistance SNP in both rats and mice confers resistance to all first-generation anticoagulants, although the actual degree of resistance may vary. Some SNPs in both rats and mice also confer resistance to the second-generation compounds bromadiolone and difenacoum. A number of SNPs have been found which have no effect on anticoagulant susceptibility.
The RRAC has carried out a series of studies, in collaboration with leading resistance experts, to determine the degree of resistance conferred by some of the most important resistance SNPs using the BCR technology it has developed (see Technical Monograph at www.rrac.info). The following tables provide data on the degree of resistance, respectively, in known resistant strains of the Norway rat and the house mouse. Resistance factors given are the multiples in the dose of the respective compound, which is required to cause a certain level of disturbed blood clotting in animals of the homozygous resistant strain in comparison to the baseline susceptible strain (see Table 2 and Table 3 and Table 4 and Table 5). RF below 1.0 means that the tested strain responded a little bit more to the experimental treatment with the anticoagulant than the baseline strain. RF = 1.0 means that there is no difference between the tested strain and the baseline susceptible strain. RF between 1 and below 2 means that there is only a minor difference, which will not noticeably influence the product performance. Higher resistance factors may be indicators of practical control problems, depending on the compound concerned.